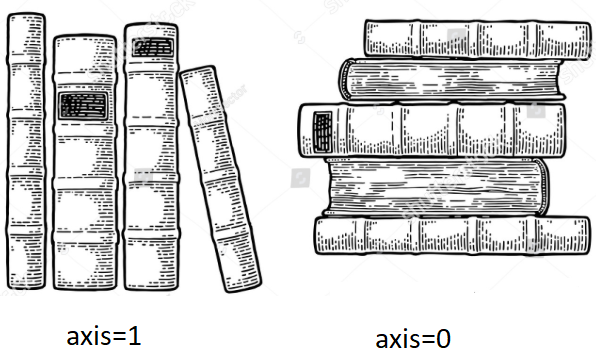
- axis=0
It will act on all the ROWS in each column, means along "indexes".
It's a row-wise operation.
- axis=1
It will act on all the COLUMNS in each row, means along "columns".
It's a column-wise operation.
a = np.array([[1, 2]])
b = np.array([[5, 6]])
row_wise=np.concatenate((a, b), axis=0)
column_wise=np.concatenate((a, b), axis=1)
print(row_wise)
print(column_wise)
>>>
[[1 2]
[5 6]]
[[1 2 5 6]]- multi array
m=np.array([[[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]],
[[10,11,12],
[13,14,15],
[16,17,18]]])
n=np.array([[[51,52,53],
[54,55,56],
[57,58,59]],
[[110,111,112],
[113,114,115],
[116,117,118]]])
np.array([m,n])
>>>
array([[[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6],
[ 7, 8, 9]],
[[ 10, 11, 12],
[ 13, 14, 15],
[ 16, 17, 18]]],
[[[ 51, 52, 53],
[ 54, 55, 56],
[ 57, 58, 59]],
[[110, 111, 112],
[113, 114, 115],
[116, 117, 118]]]])np.array([m,n]).shape
>>>
(2, 2, 3, 3)
- axis : integer, the axis along which you want to stack the arrays. -1 means last dimension. e.g. for 2D arrays axis 1 and -1 are same.
np.array([m,n]).shape
>>>
(2, 2, 3, 3)
axis 0th, 1th, 2nd, 3rd| array( [ [ [ [ element ] ] ] ]) |
case1.
axis=0
np.stack((m,n),axis=0)
array([[[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6],
[ 7, 8, 9]],
[[ 51, 52, 53],
[ 54, 55, 56],
[ 57, 58, 59]]]
case2.
axis=1
np.stack((m,n),axis=1)
array([[[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6],
[ 7, 8, 9]],
[[ 51, 52, 53],
[ 54, 55, 56],
[ 57, 58, 59]]]
case3.
axis=2
np.stack((m,n),axis=2)
array([[[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6],
[ 7, 8, 9]],
[[ 51, 52, 53],
[ 54, 55, 56],
[ 57, 58, 59]]]
case4.
axis=3
np.stack((m,n),axis=3)
array([[[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6],
[ 7, 8, 9]],
[[ 51, 52, 53],
[ 54, 55, 56],
[ 57, 58, 59]]]
reference : https://stackoverflow.com/questions/22149584/what-does-axis-in-pandas-mean
- expand_dims
Expand the shape of an array.
Insert a new axis that will appear at the axis position in the expanded array shape.
x = np.array([1, 2])
y = np.expand_dims(x, axis=(0, 1))
print(y.shape)
print(y)
>>>
(1, 1, 2)
[[[1 2]]]axis=(0, 1) : Put the 1-d in the 0th, 1th
∴
[0th, 1th, 2th]
(2,)->(1, 1, 2)
[[[1 2]]]axis=(2,0) : Put the 1-d in the 2th, 0th
∴
[0th, 1th, 2th]
(2,)->(1, 2, 1)
[[[1]
[2]]]
'Analyze Data > Python Libraries' 카테고리의 다른 글
| numpy-linspace, interp (0) | 2023.05.30 |
|---|---|
| numpy-np.c_[] VS np.r_[] (0) | 2023.05.25 |
| numpy-random (0) | 2022.12.29 |
| numpy-empty, where, allclose, dot, argsort, corrcoef, astype, nan, hstack, argmax (0) | 2022.12.07 |
| numpy-ndim, ravel, permutation, clip, subtract (0) | 2022.05.10 |