- pandas
It is a software library written for the Python programming language for data manipulation and analysis. In particular, it offers data structures and operations for manipulating numerical tables and time series.
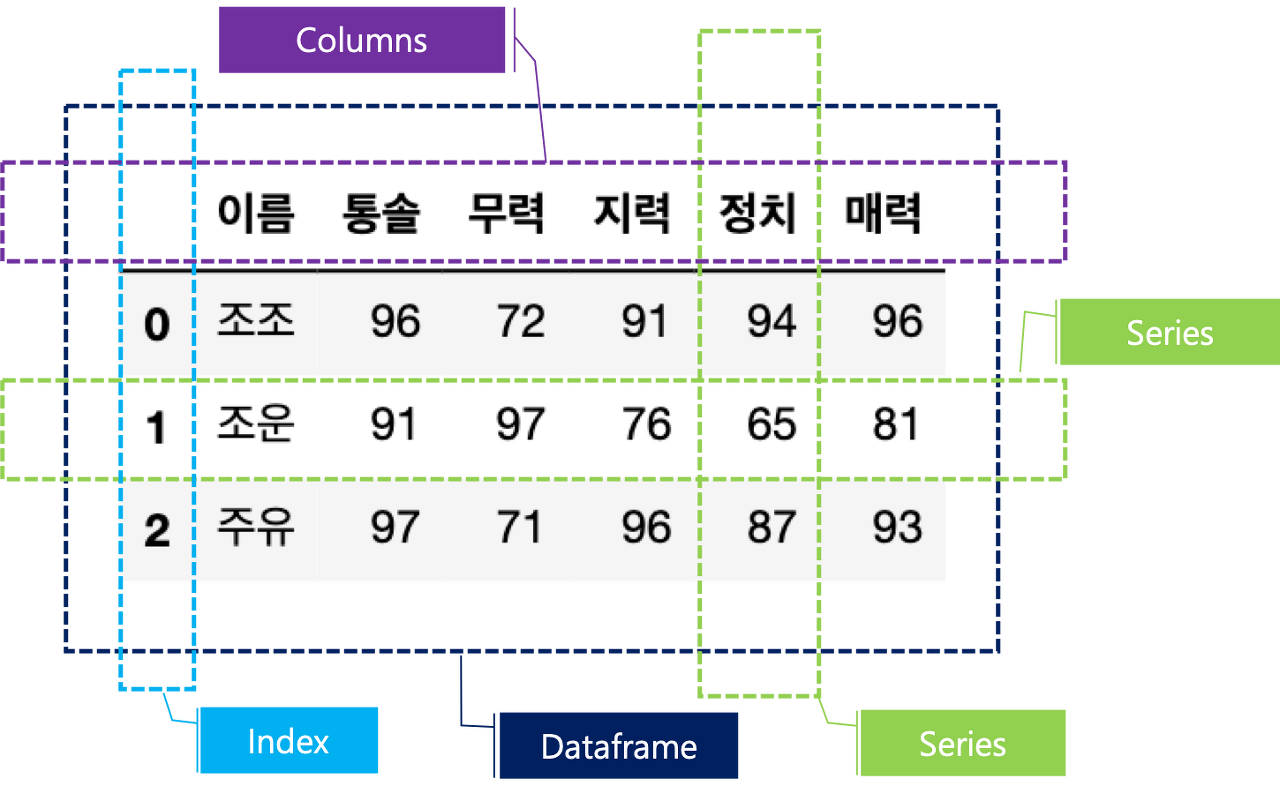
1. Series
One-dimensional array with values and index can be granted to each values.
import pandas as pd
sr=pd.Series([1000,2000,3000,4000],index=['aaa','bbb','ccc','ddd'])
sr
>>>aaa 1000
bbb 2000
ccc 3000
ddd 4000
dtype: int64import pandas as pd
infos={'name':'jojo','governance':'91'}
pd.Series(infos)
>>>
name jojo
governance 91When change the values of Series, it uses tuple.
a[['attractiveness','politics']]=(100,200)
a
>>>
name jangbi
governance 90
politics 200
attractiveness 100
- reindex
Change the sequence.
import pandas as pd
infos={'name':'jojo','governance':91,'politics':80}
s1=pd.Series(infos)
s1
>>>
name jojo
governance 91
politics 80
s1=s1.reindex(['name','politics'])
s1
>>>
name jojo
politics 80
governance 91
- isnull
Detect missing values. It return True if there is missing values. It returns bool.
a.isnull()
>>>
name False
governance False
politics False
attractiveness Falsedf.isnull().values.any()
- notnull
Detect existing (non-missing) values. It return True if there is existing (non-missing) values. It returns bool.
a.notnull()
>>>
name True
governance True
politics True
attractiveness True
- fillna
It replaces all NaN elements with other value using inplace=True.
s.fillna(5,inplace=True)
s
>>>
0 1.0
1 2.0
2 3.0
3 5.0
4 1.0
5 2.0
6 3.0
7 5.0
8 1.0
9 2.0
10 3.0
11 5.0
dtype: float64- method='ffill' : Forward Fill, fill the NaN with forward value.
- method='bfill' : Backward Fill, fill the NaN with backward value.
- drop
Delete the index and value using inplace=True
a.drop('governance', inplace=True)
a
>>>
politics 200
attractiveness 100
- dropna
Drop NaN value.
- how=all : Drop all NaN
- randn
Random Normal, generates a matrix filled with random floats samples from a normal distribution of mean 0 and variance 1.
s=pd.Series(np.random.randn(10))
s
>>>
0 -0.139915
1 0.756593
2 3.953420
3 0.059873
4 -0.536376
5 1.089905
6 0.143042
7 -0.309413
8 -0.273029
9 0.696348| 함수 | 설명 |
| rand(d0, d1, …, dn) | 주어진 차원으로 임의의 값을 반환 |
| randn(d0, d1, …, dn) | "표준 정규"분포에서 주어진 차원으로 임의의 값을 반환 |
| randint(start, stop) | Return a randum number between start and stop |
| random_sample([size]) | 0.0 <= val < 1.0 사이의 float을 size 만큼 반환 |
| random([size]) | 0.0 <= val < 1.0 사이의 float을 size 만큼 반환 |
- describe
Generate descriptive statistics including those that summarize the central tendency, dispersion and shape of a dataset's distribution, excluding NaN values.
s.describe()
>>>
count 10.000000
mean 0.544045
std 1.308795
min -0.536376
25% -0.239750
50% 0.101457
75% 0.741532
max 3.953420
- nan
Not a Number, it doesn't count.
s=pd.Series([1,2,3,np.nan]*3)
s
>>>
0 1.0
1 2.0
2 3.0
3 NaN
4 1.0
5 2.0
6 3.0
7 NaN
8 1.0
9 2.0
10 3.0
11 NaN
- value_counts
Return a Series containing counts of unique values in descending order so that the first element is the most frequently-occurring element. Excludes NA values by default.
- dropna=False : It shows NaN index values.
s=pd.Series([1,2,3,np.nan]*3)
s.value_counts(dropna=False)
>>>
3.0 3
NaN 3
2.0 3
1.0 3
- normalize=True : It contains the frequencies of the unique values.
s.value_counts(normalize=True)
>>>
3.0 0.333333
2.0 0.333333
1.0 0.333333
- map
Mapping the values.
mapping={1:'high',2:'mid',3:'low',5:'other'}
s.map(mapping)
s.map('class is {0}'.format)
>>>
0 class is 1
1 class is 2
2 class is 3
3 class is 1
4 class is 2
5 class is 3
6 class is 1
7 class is 2
8 class is 3list(s.map(lambda x:x**2))
>>>
[1, 4, 9, 1, 4, 9, 1, 4, 9]
- apply
It used when it calls the function.
def calc(value):
return value+10
s.apply(calc)
0 11
1 12
2 13
3 11
4 12
5 13
6 11
7 12
8 13
dtype: int64s.apply(lambda value:value+5)
0 6
1 7
2 8
3 6
4 7
5 8
6 6
7 7
8 8
dtype: int64def calc(value, par):
return value+par
s.apply(calc, args=(5,))
0 6
1 7
2 8
3 6
4 7
5 8
6 6
7 7
8 8
dtype: int64
- concat
Concatenate, merging two Pandas Series into a DataFrame creates a DataFrame with the two Series as columns.
df=pd.concat([IP,PORT], axis=1)
df.head()
>>>
IP Port
0 183.203.180.184 80
1 95.174.64.70 80
2 185.13.223.1 80
3 45.152.182.114 80
4 106.75.7.109 443
- unique
Return unique values of series.
NTM_df['DRULE_ATT_TYPE_CODE1'].unique()
>>>
array(['Attack', 'Malwr'], dtype=object)'Analyze Data > Python Libraries' 카테고리의 다른 글
| pandas-5. json_normalize (0) | 2021.10.25 |
|---|---|
| mlxtend-TransactionEncoder, association_rules (0) | 2021.06.23 |
| pandas-4. read_csv, unique, to_csv, file upload, file download (0) | 2021.06.22 |
| numpy-array, arange, reshape, slicing, newaxis, ...(Ellipsis) (0) | 2021.05.25 |
| pandas-2. DataFrame (0) | 2021.05.25 |