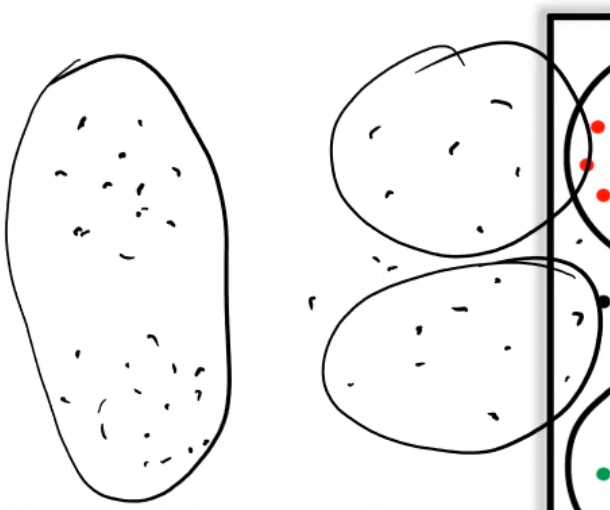
- Here we have two clusters, a dense set of points, and one cluster, a loose set of points.

- In this case, K-Means Clustering cannot cope with different densities such as the figure below.
- Density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN)
- The algorithm is based on the Density-based clustering.
- Can find an arbitrary shape of cluster.
- It can cope with different densities such as the figure below.
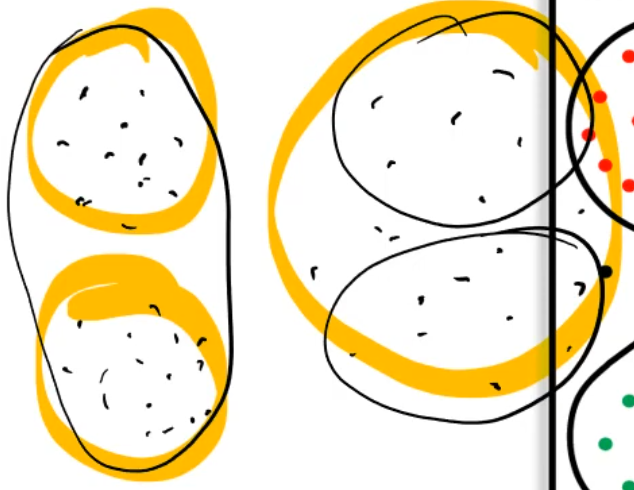
- With the K-Means Clustering, all objects must be assigned to some cluster. In other words, no object is assigned to any cluster. But In this algorithm, there are objects that are not assigned(noise) to any cluster.
- Can remove noise from clustering results.
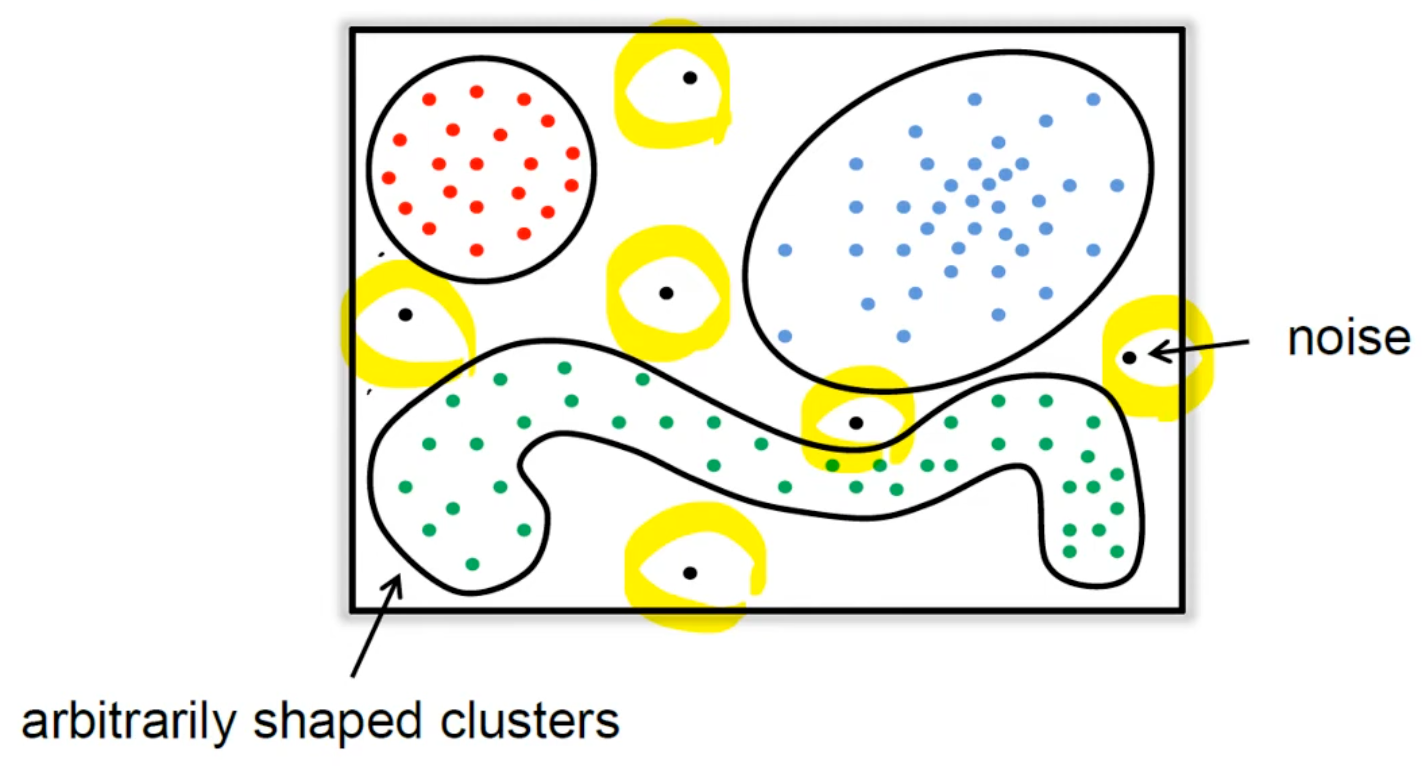
- Clusters are the collections of data points with high density.
- Density around a noise point is very low.
- Quantify the features of clusters and noise points to find a set of valid clusters.
- Definition 1 (Naïve Approach).
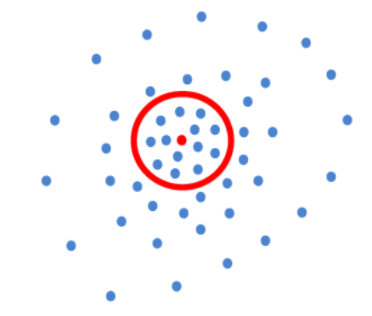
- All points within the epsilon radius are the epsilon neighbors of p.
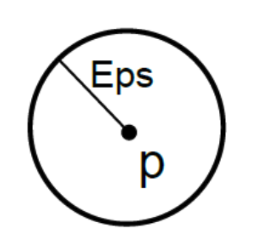
- Around this red point, all points in the radius are epsilon neighbors of the red point.
- Problem of Definition 1 (Naïve Approach)
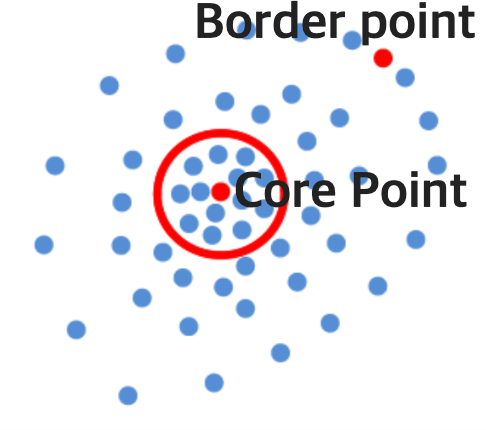
- There are two kinds of points in a cluster : Points inside of the cluster (core points), Points on the border of the cluster (border points)
- An ε-neighborhood of a border point contains significantly less points than an ε- neighborhood of a core point.
- Based on an arbitrary point (core point), the appsilon within the radius of that point becomes one cluster only when there must be more than the minimum number of points we set.
- Definition 2 (Directly Density-Reachable)
- Point p(border point) is inside the ε-neighborhood of point q(core point).
- In other words, border points are connected to core points.
- The density around the core points should be high.

For example,
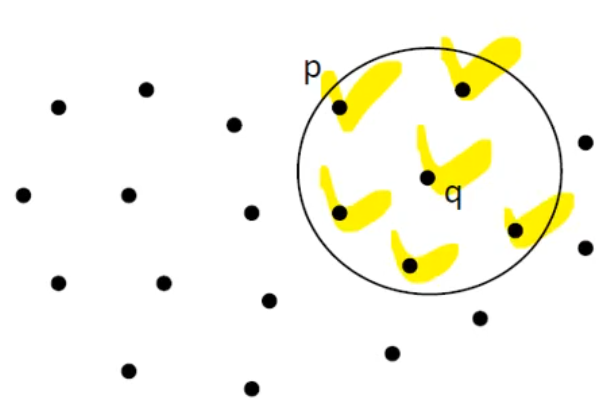
- So, in this case, two conditions are satisfied(including the point 'q' itself).
- Problem of Definition 2 (Directly Density-Reachable)

However,
- Definition 3 (Density-Reachable)

- A point p1 is directly density-reachable from a point q.
- A point p is directly density-reachable from a point p1.
- A point p is not directly density-reachable from a point q, but density-reachable.
| A point p is density-reachable from a point q with regard to the parameters 𝜖 and MinPts, if there is a chain of points p1, p2, ..., ps |
- Definition 4 (Density-Connected)

- Point p and q share one point v.
- Point p is density reachable from point v.
- Point q is density reachable from point v.
- Thus, point p and point q are density-connected.
- Definition 5 (Cluster)

- Procedure
| 1: Select any one arbitraty points as the initial centroids. 2: Expand the points that can be density-connected. 3: Extend until there is no longer a point that can be density-connected. 4: In this way, one cluster is completed. 5: Move to another arbitrary point 6: repeat |
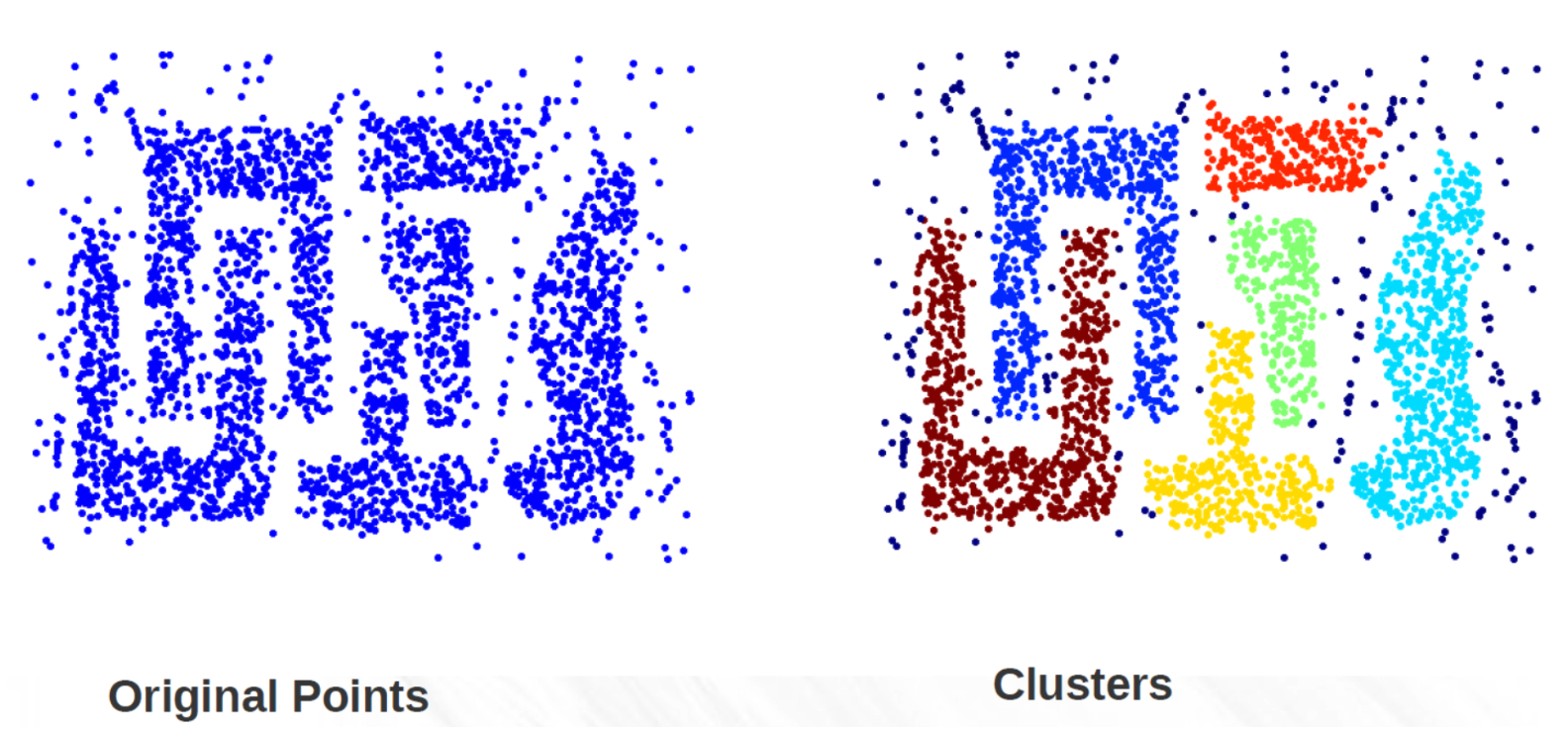
- Result
'Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| K-Means Clustering(KMC) (0) | 2025.11.07 |
|---|---|
| Transfer learning (0) | 2024.01.09 |
| Backpropagation, chain rule (0) | 2023.12.14 |
| Sigmoid, Softmax, Cross entropy (0) | 2023.12.05 |
| Entropy, Cross-Entropy, Binary cross entropy, SparseCategoricalCrossentropy (0) | 2023.12.01 |