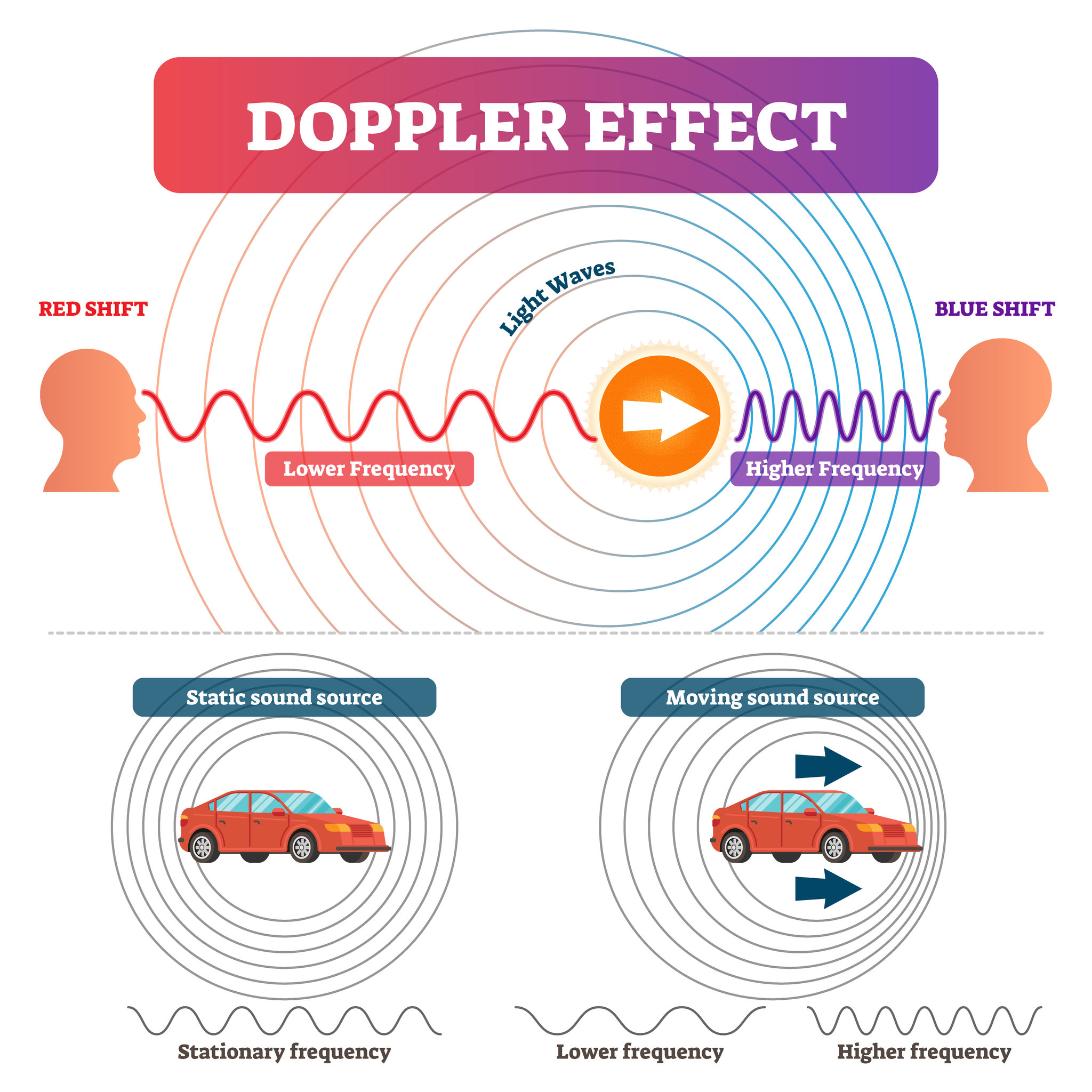
- Doppler Effect
The apparent change in the frequency of a wave caused by relative motion between the source of the wave and the observer.
If the object is moving towards a stationary observer,

these bunched up waves are observed at a high frequency,

if the object is moving away from a stationary observer,

the waves are observed at a lower frequency.

- Doppler Effect with sound
For example,
As the vehicle's coming towards you, the sound waves that it's emitting bunch up, and so are delivered to you at a
higher frequency, which you interpret as a higher pitch, because the frequency of sound waves is pitch.

and then when the vehicle passes you and is moving away from you, the sound waves spread out, and so you hear them at a lower frequency – a lower pitch.

- Doppler Effect with light
Higher-frequency light waves means bluer light, and lower-frequency light waves
means redder light.
- Red-shift
A spectrum shows the seven colours making up visible light. A spectroscope can be used to view the absorption spectrum for any light emitting object. Dark lines would be seen in the spectrum where light at that frequency and wavelength has been absorbed.
If we looked at the absorption spectrum for light on Earth emitted by our closest star, the Sun, we would observe dark lines in specific positions.
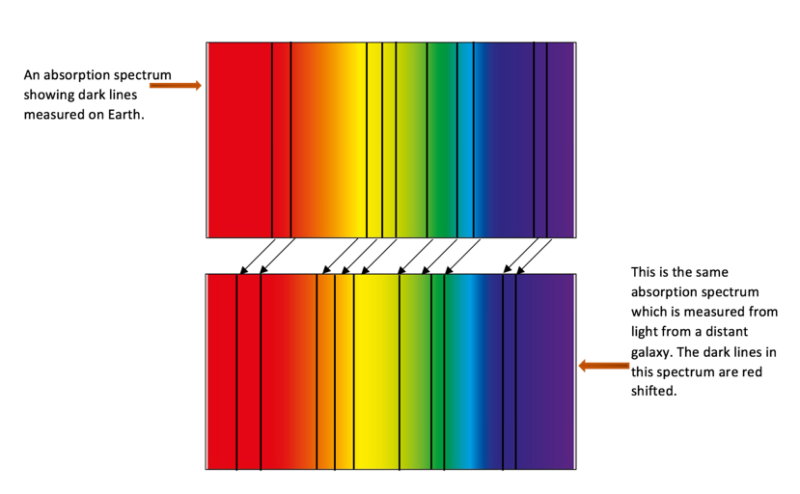
This shift towards the red end of the spectrum is the effect known as red-shift. It occurs because the galaxy is moving away from us and we are moving away from it at the same time.
The greater the red-shift, the further and faster the star is moving away from us.
- Doppler Effect Formula

1. Example : Source Moving Towards the Observer at Rest
In this case, the observer’s velocity is zero, so V0 is equal to zero.

2. Example : Source Moving Away from the Observer at Rest
The source moves away from the observer, so its velocity is negative to indicate the direction.
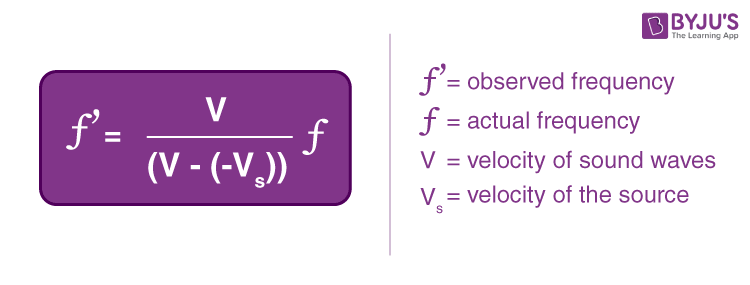
3. Example : Observer Moving Towards a Stationary Source
Vs will equal to zero.
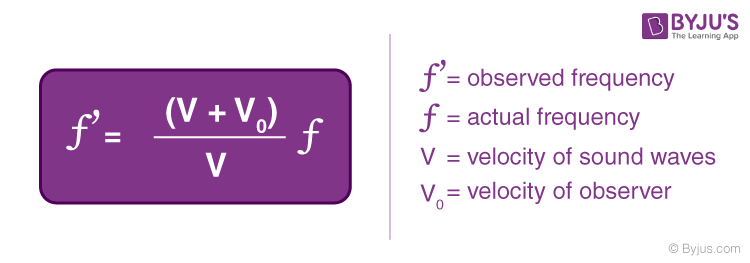
4. Example : Observer Moving Away from a Stationary Source
Since the observer is moving away, the velocity of the observer becomes negative.
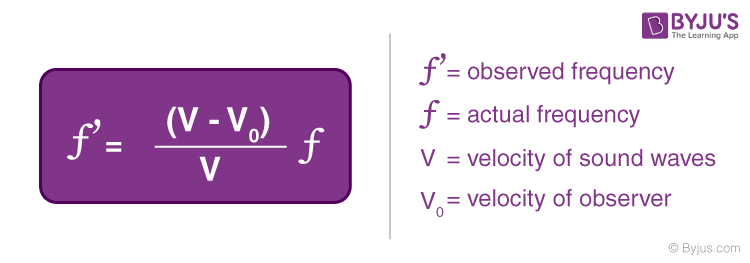
https://online-learning-college.com/knowledge-hub/gcses/gcse-physics-help/doppler-effect/
https://byjus.com/physics/doppler-effect/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h4OnBYrbCjY
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-doppler-effect-and-doppler-shift/
'Concept' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CPU VS GPU VS TPU, What is CUDA? (0) | 2023.04.14 |
|---|---|
| Web Scraping, Web Crawling, IP (0) | 2021.05.18 |
| YAML, YML (0) | 2021.04.26 |
| GUI, Polling, UDP (0) | 2021.04.20 |