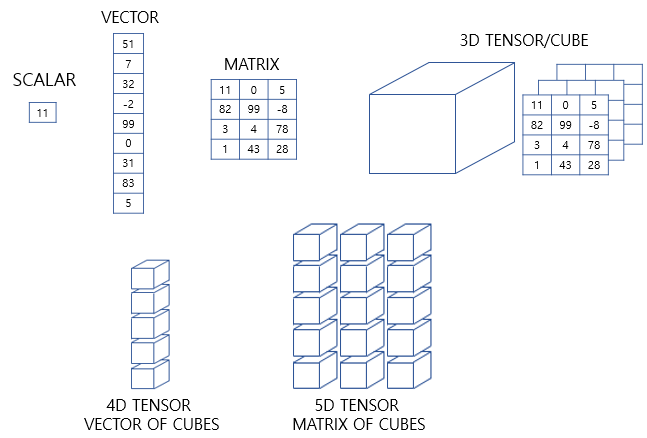

- id-tensor = vector
- 2d-tensor = matrix
- 3d-tensor = tensor
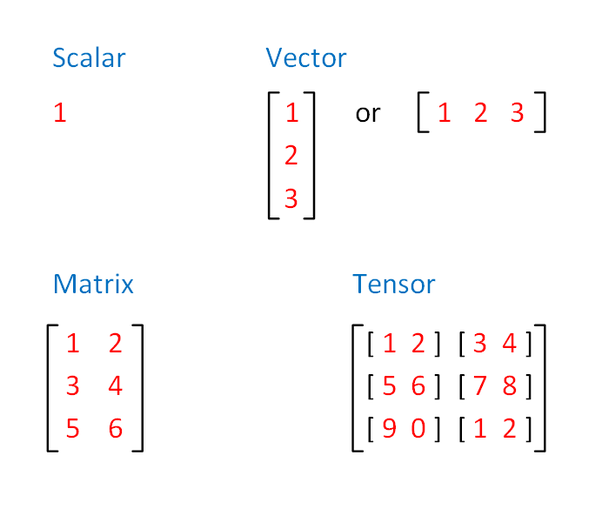
- Scalar
0-dimensional, a data consisting of a single real value. For example, your speed is a scalar value because it only has one component, how fast you are going. Your height is also a scalar value because the only component is how tall you are.
- Vector
1-dimensional array or list. 1-dimensional tensor.
np.array([1,2,3])
>>>
array([1, 2, 3])
- Matrix
2-dimensional which has row and column.
np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
>>>
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
- Tensor
Over 3-dimensional
np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[7,8,9],[10,11,12]]])
>>>
array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]]])
- Matrix Operation
Hypothesis : Predict one y with multiple x.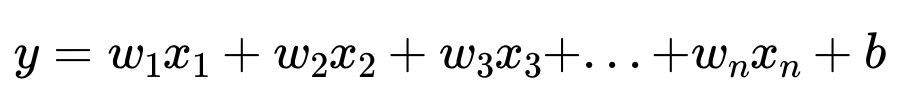 |
It can be expressed as vectors.
 Or  |
Let's take this.
Hypothesis : Predict one y with multiple x. |
H(X)=XW+B And added B. 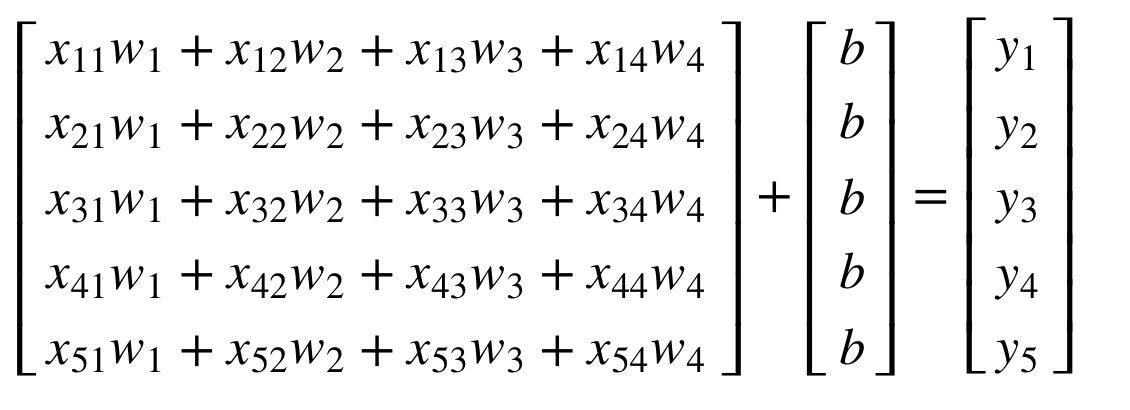 |
Or
H(X)=WX+B |
For instance, (batch_dim, input_dim) * (input_dim, output_dim) + b = (batch_dim, output_dim)
dimension : output_dim = b
For instance,
(1, 4) * (4, 2) + 2 = (1, 2)
(5, 4) * (4, 3) + (5, 3) = (5, 3)
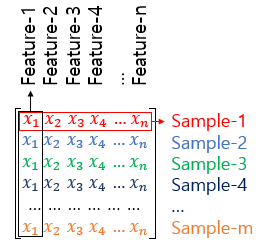
- sample
Divided data into coutable units.
- feature
Each x(independent variable).
https://holamundo.tistory.com/manage/newpost/74?type=post&returnURL=ENTRY
'Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Entropy, Cross-Entropy (0) | 2021.03.31 |
|---|---|
| Support Vector Machine, Margin, Kernel, Regularization, Gamma (0) | 2021.03.30 |
| Softmax Regression, Cross Entropy (0) | 2021.03.24 |
| Logistic Regression, Sigmoid function (0) | 2021.03.17 |
| Linear Regression, Simple Linear Regression, Multiple Linear Regression, MSE, Cost function, Loss function, Objective function, Optimizer, Gradient Descent (0) | 2021.03.16 |