- 2D Transformations

A method used to model the matching relationship between two images directly on a 2D plane.

- Rigid Transformation(Euclidean transformation)
Only change its position and orientation while maintaining its shape and size.
In other words, it is a transformation that only allows rotation and translation.
- Translation


- Degree of Freedom(DOF) : t1, t2
- Shearing

If you want to scale the figure image on the left side by a multiple of the horizontal and vertical b times as shown on the right side, you can apply x'=ax and y' = bx.

- Rotation

- A transformation matrix that rotates (x, y) counterclockwise by θ radian. The object is spinning based on (0,0).
- Degree of Freedom(DOF) : 1, therefore, only one matching pair can determine the rotational transformation.
- considering scale change
- Euclidean

- Degree of Freedom(DOF) :
- Rigid

Translation + Rotation
Rotate by θ around the origin of the image and then move in parallel to the original position.
The degree of freedom of the rotational transformation is 3. It requires at least 2 matching pairs.
c : tx + rotation
d : ty + rotation
[tx, ty] : translation
- Similarity

- Degree of Freedom(DOF) :
- Convert to homogeneous coordinate system
In order to be a single matrix from Rotation + Translation + Scaling
- Affine Transformation

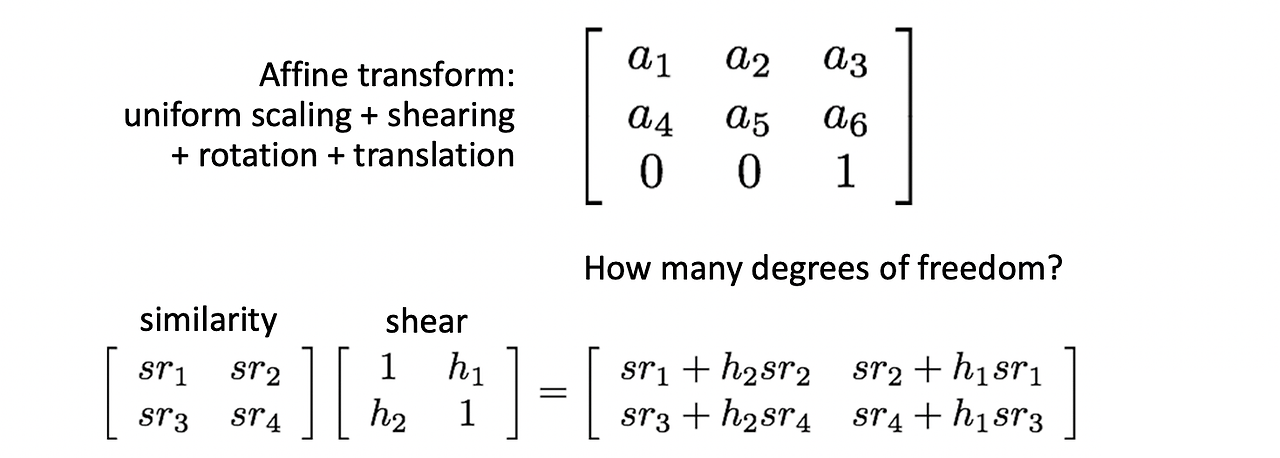
- A transformation that preserves linearity, length (distance) ratio, and parallelism.
- Degree of Freedom(DOF) : 6,
- Convert to homogeneous coordinate system
- Homograpy (Projective Transformation)


If a planar surface is projected as an image A and an image B for different camera positions, the relationship between the image A and the image B may be expressed as a homography.

https://velog.io/@richpin/Computer-Vision-07-2D-Transformations
'Autonomous Vehicle > Video Geometry' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Homography (0) | 2024.07.25 |
|---|---|
| Camera Calibration (0) | 2024.07.23 |
| 3D Transformations (0) | 2024.07.19 |
| Coordinate System (0) | 2024.07.18 |
| Epipolar Geometry (0) | 2023.09.11 |